nf-core/rnafusion
RNA-seq analysis pipeline for detection of gene-fusions
3.0.2). The latest
stable release is
3.0.1b
.
Introduction
This document describes the output produced by the pipeline. Most of the plots are taken from the MultiQC report, which summarises results at the end of the pipeline.
The directories listed below will be created in the results directory after the pipeline has finished. All paths are relative to the top-level results directory.
Pipeline overview
The pipeline is built using Nextflow and processes data using the following steps:
- Download and build references - Build references needed to run the rest of the pipeline
- STAR - Alignment for arriba, and STAR-fusion
- Cat - Concatenate fastq files per sample ID
- Arriba - Arriba fusion detection
- STAR-fusion - STAR-fusion fusion detection
- StringTie - StringTie assembly
- FusionCatcher - Fusion catcher fusion detection
- Samtools - SAM/BAM file manipulation
- Fusion-report - Summary of the findings of each tool and comparison to COSMIC, Mitelman, FusionGBD and FusionGDB2 databases
- FusionInspector - Supervised analysis of fusion predictions from fusion-report, recover and re-score evidence for such predictions
- Arriba visualisation - Arriba visualisation report for FusionInspector fusions
- Picard - Collect QC metrics
- FastQC - Raw read quality control
- MultiQC - Aggregate reports describing QC results from the whole pipeline
- Pipeline information - Report metrics generated during the workflow execution
Download and build references
Output reference files and folder structure
References directory structure
references/arribablacklist_hg38_GRCh38_v2.1.0.tsv.gzprotein_domains_hg38_GRCh38_v2.1.0.gff3cytobands_hg38_GRCh38_v2.1.0.tsv
ensemblHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.all.faHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.cdna.all.fa.gzHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.gtfHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.chr.gtfHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.chr.gtf.refflatHomo_sapiens.GRCh38.{ensembl_version}.interval_list
fusioncatcherhuman_v<version>- dir with all references for fusioncatcher
fusion_report_dbcosmic.dbfusiongdb.dbfusiongdb2.dbmitelman.db
star- dir with STAR indexstarfusion- files and dirs used to build the index
ctat_genome_lib_build_dir- dir containing the index
(Only files or folders used by the pipeline are mentioned explicitly.)
Main pipeline workflow
If no argument is specified here, the tool was used with default parameters.
Directory structure
{outdir}
├── arriba
├── arriba_visualisation
├── cram_arriba
├── cram_starfusion
├── fastp
├── fastqc
├── fusioncatcher
├── fusioninspector
├── fusionreport
├── kallisto_quant
├── megafusion
├── multiqc
├── picard
├── pipeline_info
├── samtools_sort_for_arriba
├── star_for_arriba
├── star_for_starfusion
├── starfusion
└── work
.nextflow.logIf no parameters are specified, the default is applied.
Arriba
Arriba is used for i) detect gene fusions and ii) create a PDF report for the fusions found (visualisation):
Detection
Output files
arriba/<sample>.arriba.fusions.tsv- contains the identified fusions<sample>.arriba.fusions.discarded.tsv
Visualisation
Output files
arriba_visualisation/<sample>_combined_fusions_arriba_visualisation.pdf
The visualisation displays the fusions that fusioninspector outputs. That means that fusions from all callers are aggregated (by fusion-report) and then analyzed through fusioninspector (Note: Fusioninspecor contains a filtering step!).
Cat
Output files
cat/<sample>_1.merged.fastq.gz<sample>_2.merged.fastq.gz
If multiple libraries or runs have been provided for the same sample in the input samplesheet (e.g. to increase sequencing depth) then these will be merged at the very beginning of the pipeline in order to have consistent sample naming throughout the pipeline. Please refer to the usage documentation to see how to specify these samples in the input samplesheet.
Fastp
If --trim_fastp is selected, fastp will filter low quality reads as well as bases at the 5’ and 3’ ends, trim adapters (automatically detected, but input with parameter --adapter_fasta is possible). 3’ trimming is also possible via parameter --trim_tail.
Output files
fastp/<sample>_1.fastp.fastq.gz<sample>_2.fastp.fastq.gz<sample>.fastp.html<sample>.fastp.json<sample>.fastp.log
FastQC
Output files
fastqc/*_fastqc.html: FastQC report containing quality metrics.*_fastqc.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report, tab-delimited data file and plot images.
FastQC gives general quality metrics about your sequenced reads. It provides information about the quality score distribution across your reads, per base sequence content (%A/T/G/C), adapter contamination and overrepresented sequences. For further reading and documentation see the FastQC help pages.
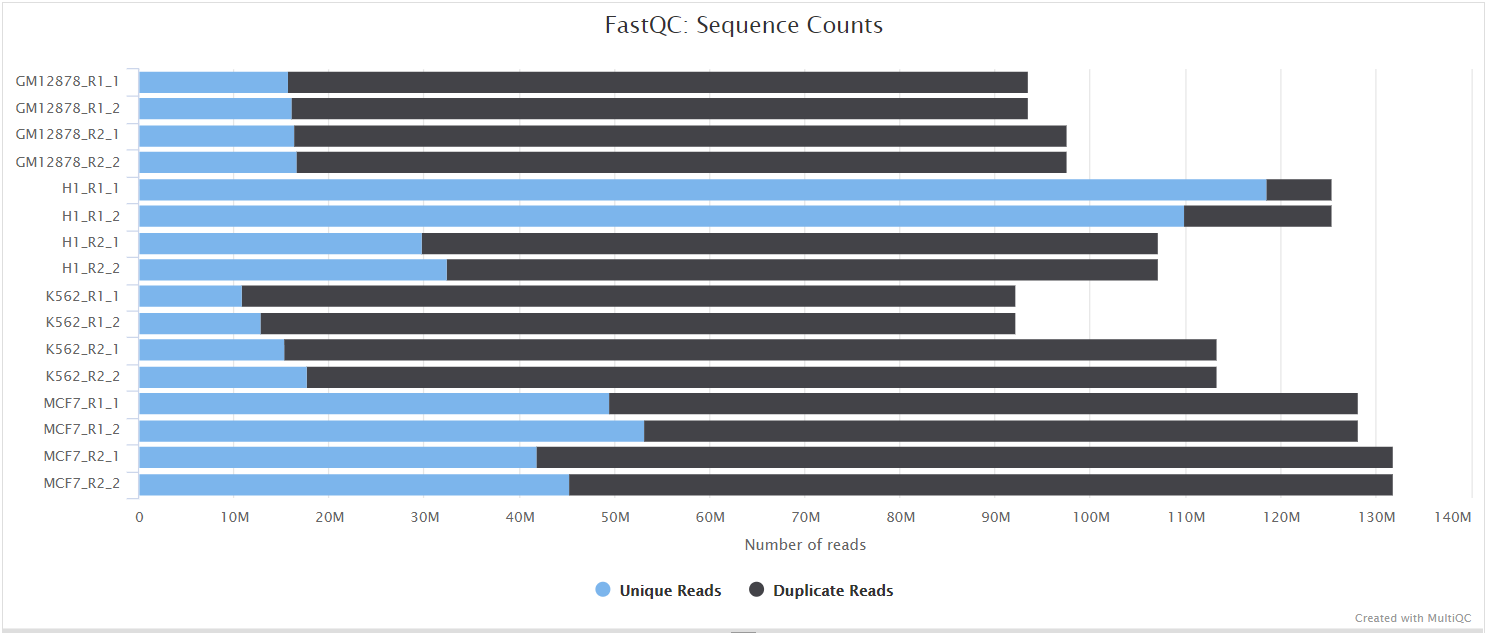
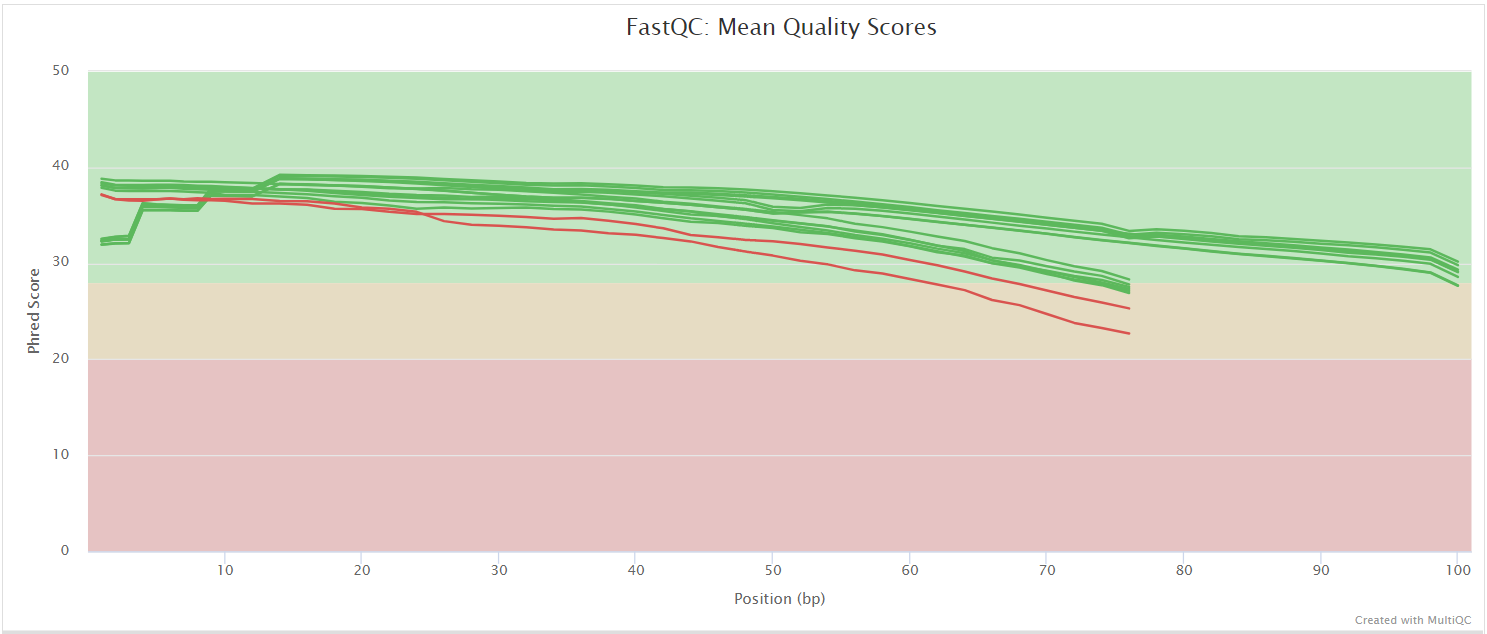
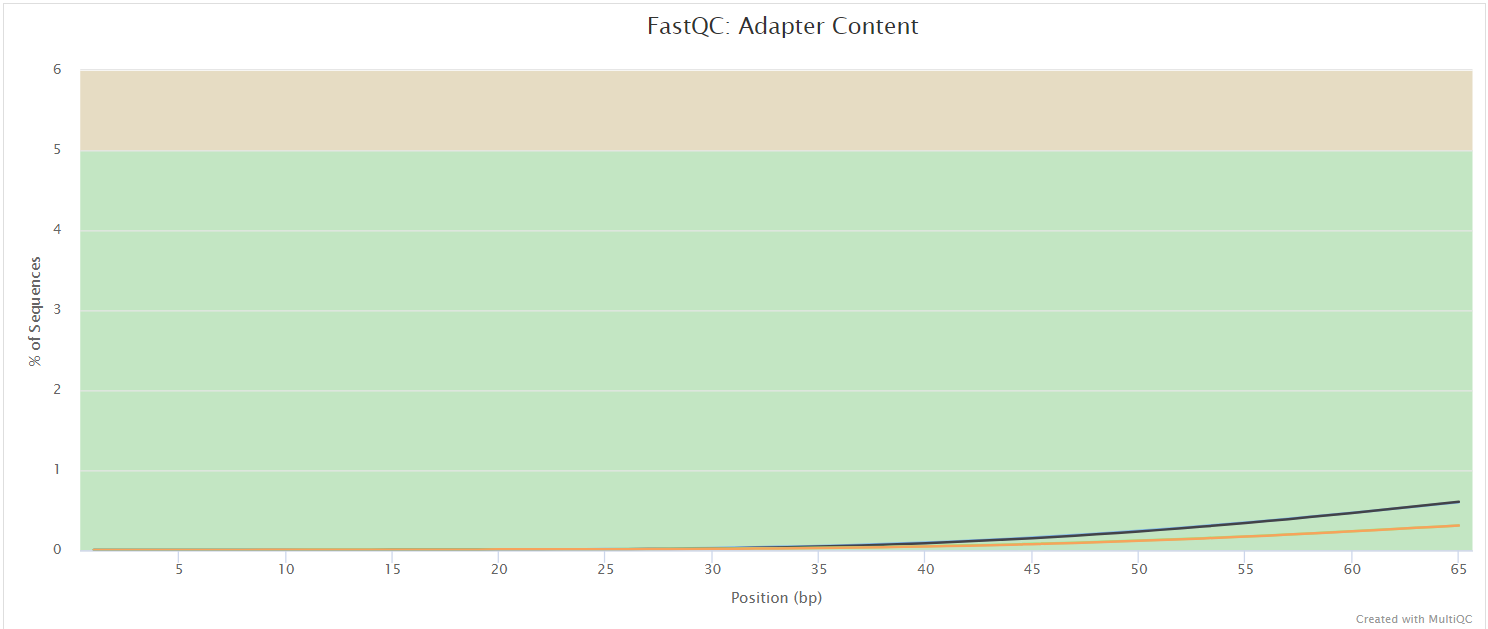
The FastQC plots displayed in the MultiQC report shows untrimmed reads. They may contain adapter sequence and potentially regions with low quality.
FusionCatcher
Output files
fusioncatcher<sample>.fusioncatcher.fusion-genes.txt<sample>.fusioncatcher.summary.txt<sample>.fusioncatcher.log
FusionCatcher searches for novel/known somatic fusion genes translocations, and chimeras in RNA-seq data. Possibility to use parameter --fusioncatcher_limitSjdbInsertNsj to modify limitSjdbInsertNsj.
FusionInspector
Output files
fusioninspector<sample>.fusion_inspector_web.html- visualisation report described in details hereFusionInspector.log<sample>.FusionInspector.fusions.abridged.tsv
FusionInspector performs a validation of fusion transcript predictions. Possibility to use --fusioninspector_limitSjdbInsertNsj to set limitSjdbInsertNsj to anything other than the default 1000000.
Fusion-report
Please note that fusion-report is executed from fork https://github.com/Clinical-Genomics/fusion-report
Output files
fusionreport-
- ` .fusionreport.tsv` - ` .fusionreport_filtered.tsv` - ` _fusionreport_index.html` - general report for all filtered fusions - ` .fusions.csv` - index in csv format - ` _ .html` - specific report for each filtered fusion
-
Fusion-report is a tool for parsing outputs from fusion detection tools. The score is explained here: https://github.com/Clinical-Genomics/fusion-report/blob/master/docs/score.md. Summary:
The weights for databases are as follows:
- COSMIC (50)
- MITELMAN (50)
- FusionGDB2 (0)
The final formula for calculating score is:
All tools have the same weight.
Kallisto
Output files
kallisto<sample>.kallisto_quant.fusions.txt
Quantifying abundances of transcripts from bulk and single-cell RNA-Seq data, or more generally of target sequences using high-throughput sequencing reads.
Vcf_collect
Output files
vcf_collect<sample>_fusion_data.vcf- contains the fusions in vcf format with collected statistics.
Vcf-collect takes as input the results of fusion-report and fusioninspector. That means fusions from all tools are aggregated. Fusioninspector applies a filter so it is possible some fusions detected by a caller are not filtered out by fusioninspector. In those cases, vcf-collect will display the fusions, but a lot of data will be missing as fusioninspector performs the analysis for each fusion.
Megafusion converts RNA fusion files to SV VCF and collects statistics and metrics in a VCF file.
MultiQC
Output files
multiqc/multiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.multiqc_data/: directory containing parsed statistics from the different tools used in the pipeline.multiqc_plots/: directory containing static images from the report in various formats.
MultiQC is a visualization tool that generates a single HTML report summarising all samples in your project. Most of the pipeline QC results are visualised in the report and further statistics are available in the report data directory.
Results generated by MultiQC collate pipeline QC from supported tools e.g. FastQC. The pipeline has special steps which also allow the software versions to be reported in the MultiQC output for future traceability. For more information about how to use MultiQC reports, see http://multiqc.info.
Picard
Output files
Picard CollectRnaMetrics and picard MarkDuplicates share the same output directory.
picard<sample>.MarkDuplicates.metrics.txt- metrics from MarkDuplicates<sample>_rna_metrics.txt- metrics from CollectRnaMetrics<sample>_insert_size_metrics.txt.txt- metrics from CollectInsertSizeMetrics<sample>.bam- BAM file with marked duplicates
Samtools
Samtools sort
Samtools sort is used to sort BAM files from STAR_FOR_STARFUSION (for arriba visualisation)
Output files
samtools_sort_for_<arriba><sample>(_chimeric)_sorted.bam- sorted BAM file
Samtools index
Samtools index is used to index BAM files from STAR_FOR_ARRIBA (for arriba visualisation) and STAR_FOR_STARFUSION (for QC)
Output files
samtools_for_<arriba/qc><sample>.(Aligned.sortedByCoord).out.bam.bai-
STAR
STAR is used to align to genome reference
STAR is run for 3 tools:
For arriba with the parameters:
--readFilesCommand zcat \
--outSAMtype BAM Unsorted \
--outSAMunmapped Within \
--outBAMcompression 0 \
--outFilterMultimapNmax 50 \
--peOverlapNbasesMin 10 \
--alignSplicedMateMapLminOverLmate 0.5 \
--alignSJstitchMismatchNmax 5 -1 5 5 \
--chimSegmentMin 10 \
--chimOutType WithinBAM HardClip \
--chimJunctionOverhangMin 10 \
--chimScoreDropMax 30 \
--chimScoreJunctionNonGTAG 0 \
--chimScoreSeparation 1 \
--chimSegmentReadGapMax 3 \
--chimMultimapNmax 50For STAR-fusion with the parameters:
--twopassMode Basic \
--outReadsUnmapped None \
--readFilesCommand zcat \
--outSAMstrandField intronMotif \
--outSAMunmapped Within \
--chimSegmentMin 12 \
--chimJunctionOverhangMin 8 \
--chimOutJunctionFormat 1 \
--alignSJDBoverhangMin 10 \
--alignMatesGapMax 100000 \
--alignIntronMax 100000 \
--alignSJstitchMismatchNmax 5 -1 5 5 \
--chimMultimapScoreRange 3 \
--chimScoreJunctionNonGTAG -4 \
--chimMultimapNmax 20 \
--chimNonchimScoreDropMin 10 \
--peOverlapNbasesMin 12 \
--peOverlapMMp 0.1 \
--alignInsertionFlush Right \
--alignSplicedMateMapLminOverLmate 0 \
--alignSplicedMateMapLmin 30 \
--chimOutType Junctions \
--quantMode GeneCountsSTAR_FOR_STARFUSION uses
${params.ensembl}/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.${params.ensembl_version}.chr.gtfwhereas STAR_FOR_ARRIBA uses${params.ensembl_ref}/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.${params.ensembl_version}.gtf
Output files
Common
star_for_<tool><sample>.Log.final.out<sample>.Log.progress.out<sample>.SJ.out.tab
For arriba:
-
<sample>.Aligned.out.bamFor starfusion:
-
<sample>.Aligned.sortedByCoord.out.bam -
<sample>.Chimeric.out.junction -
<sample>.ReadsPerGene.out.tab
The STAR index is generated with --sjdbOverhang ${params.read_length - 1}, params.read_length default is 100.
STAR-fusion
Output files
starfusion<sample>.starfusion.fusion_predictions.tsv- contains the identified fusions<sample>.starfusion.abridged.tsv- contains the identified fusions abridgedstarfusion.abridged.coding_effect.tsv
StringTie
Output files
stringtie/<sample>/stringtie.merged.gtf- merged gtf from annotation and stringtie output gtfs
Pipeline information
Output files
pipeline_info/- Reports generated by Nextflow:
execution_report.html,execution_timeline.html,execution_trace.txtandpipeline_dag.dot/pipeline_dag.svg. - Reports generated by the pipeline:
pipeline_report.html,pipeline_report.txtandsoftware_versions.yml. Thepipeline_report*files will only be present if the--email/--email_on_failparameter’s are used when running the pipeline. - Reformatted samplesheet files used as input to the pipeline:
samplesheet.valid.csv. - Parameters used by the pipeline run:
params.json.
- Reports generated by Nextflow:
Nextflow provides excellent functionality for generating various reports relevant to the running and execution of the pipeline. This will allow you to troubleshoot errors with the running of the pipeline, and also provide you with other information such as launch commands, run times and resource usage.